Selecting the right health insurance plan is crucial for accessing quality healthcare while managing costs effectively. Two of the most common types of health insurance plans in the United States are Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans and Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans. Each offers unique benefits and trade-offs. Understanding these differences helps individuals and families make informed decisions that align with their healthcare needs and financial goals. This comprehensive guide explores the key features, advantages, and considerations when choosing between HMO and PPO insurance plans.
What is an HMO Plan?
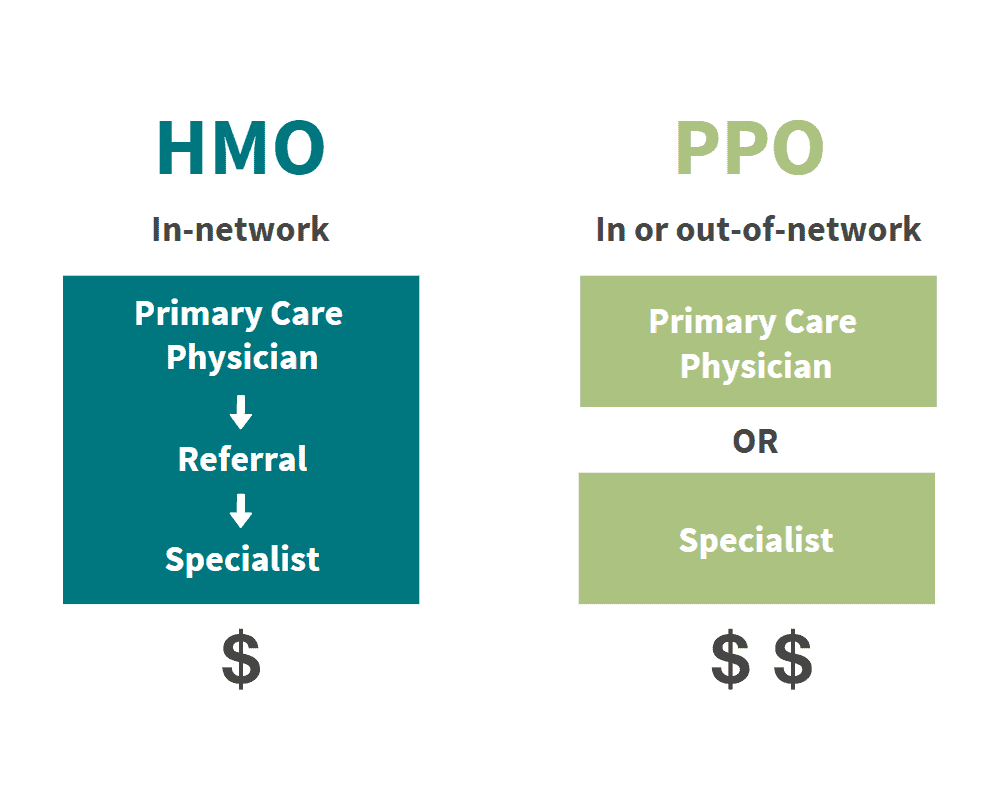
A Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plan emphasizes coordinated care through a defined network of providers. Key characteristics include:
- Network Restrictions: You must select a primary care physician (PCP) who manages your healthcare and provides referrals for specialists.
- Referrals Required: Specialist visits usually require a referral from your PCP.
- Lower Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs: HMOs generally offer lower monthly premiums and copays.
- Limited Coverage Outside Network: Services received outside the HMO network are typically not covered, except in emergencies.
HMOs focus on preventive care and streamlined services to keep costs down and encourage efficient healthcare delivery.
What is a PPO Plan?
A Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plan offers greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. Its features include:
- No PCP Requirement: You do not need to select a primary care physician.
- No Referrals Needed: You can see specialists directly without needing prior approval.
- Broader Provider Network: PPOs cover services from both in-network and out-of-network providers, though costs are lower when using in-network doctors.
- Higher Premiums and Out-of-Pocket Costs: PPO plans typically have higher premiums and deductibles.
PPOs prioritize freedom of choice and convenience, appealing to those who want control over their healthcare decisions.
Comparing HMO and PPO Plans: Advantages and Disadvantages
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Provider Network | Restricted to network | Larger network + out-of-network coverage |
| Primary Care Physician | Required | Not required |
| Referrals for Specialists | Required | Not required |
| Premium Costs | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Lower copays and deductibles | Higher copays and deductibles |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Coverage Outside Network | Very limited (except emergencies) | Covered, but at higher cost |
Who Should Choose an HMO Plan?
HMO plans suit individuals or families who:
- Prefer lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
- Are comfortable with having a primary care physician coordinate care.
- Seek a more managed and coordinated healthcare experience.
- Do not mind using a limited provider network.
- Want a focus on preventive care and wellness.
Who Should Choose a PPO Plan?
PPO plans are ideal for those who:
- Want the freedom to see any doctor or specialist without referrals.
- Travel frequently or live in multiple locations and require broader provider access.
- Are willing to pay higher premiums for flexibility and choice.
- Have existing relationships with out-of-network specialists.
- Prefer less managed care and more autonomy over healthcare decisions.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
- Budget: Evaluate how much you can afford in premiums, deductibles, and copays.
- Healthcare Needs: Consider your current health status, need for specialists, and frequency of doctor visits.
- Provider Preferences: Check if your preferred doctors and hospitals are in-network.
- Geographic Location: Some areas have limited HMO or PPO options.
- Lifestyle: Consider travel habits and whether you need nationwide coverage.
- Coordination of Care: Decide if you want a PCP to manage your care or prefer direct access to specialists.
Conclusion: Make the Choice That Fits You Best
Choosing between an HMO and PPO plan hinges on balancing cost, flexibility, and provider access. HMOs offer cost savings and coordinated care but restrict provider choice, while PPOs provide greater freedom at a higher price. Carefully assessing your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences will ensure you select the plan that delivers optimal value and peace of mind.